High-protein diet: definition, effects and sample menus
The high-protein diet encourages weight loss while maintaining muscle mass. How does it work? What kind of menus are involved?

What exactly does a high-protein diet consist of?
Like most weight-loss diets, the high-protein regime is based on reducing calorie intake.
Let’s remember that for the body to work properly, it needs a daily intake of macronutrients which are used for building cells and providing them with the energy they need to function. These macronutrients consist of:
- carbohydrates (including sugars) ;
- lipids (found in fats and oils) ;
- and proteins (found in meat and fish, amongst others.)
By focusing on protein-rich foods and reducing intake of carbohydrates and lipids, the high-protein diet produces a deficit in calories which, after a few days, results in weight loss(1).
What’s the connection between prioritising protein and losing weight?
For a diet to result in weight loss, it has to reduce daily calorie intake. A deficit of 500 kcal a day is believed to be the right level because it is large enough to force the body to draw on its reserveswithout leading to fatigue or hunger.
Each macronutrient has its own particular calorie load.
- 1g of lipids = 9 kcal;
- 1g of carbohydrates = 4 kcal;
- 1g of protein = 4 kcal.
It’s also important to understand that the process of digesting proteins uses up more energy than that of carbohydrates or lipids. This means that proteins are not only one of the nutrients with the fewest calories, but that the body burns more calories when digesting them (2). The high-protein diet was developed on this basis.
What are the effects of a high-protein diet?
The advantages
As this diet produces a deficit in calorie intake while maintaining a a high level of protein, it results in weight loss without any significant loss of muscle mass. Indeed, compared with a typical slimming diet, the high-protein approach substantially reduces muscle breakdown .
In addition, it maintains the sensation of satiety. The fact that you don’t feel hungry in between meals means you can space them out and you won’t get the urge to snack(3). Losing weight without feeling hungry makes it easier to stick to the diet over the long term.
The cravings we often experience when dieting are caused by fluctuating pancreatic hormone levels in the blood. By maintaining a low carbohydrate intake these levels stabilise and the urge to snack in between meals recedes (4).
The disadvantages
The main downside of this diet is that, in order to work well, it must be followed to the letter. You may therefore have to eat differently from those around you
When following a high-protein diet, the kidneys have to work harder than normal. So make sure you drink plenty of water to compensate for your increased protein intake.
In addition, given that the potential risks of excessive protein consumption have yet to be clearly determined, be sure to seek medical advice before starting this diet (5).
What can you eat on a high-protein diet?
The secret of this diet lies in ensuring the correct proportions for each type of macronutrient. It’s important to remember that at each meal, you need to eat three portions of protein, one of carbohydrates and one of lipids. This 3:1:1 ratio forms the basis of this new nutritional balance.
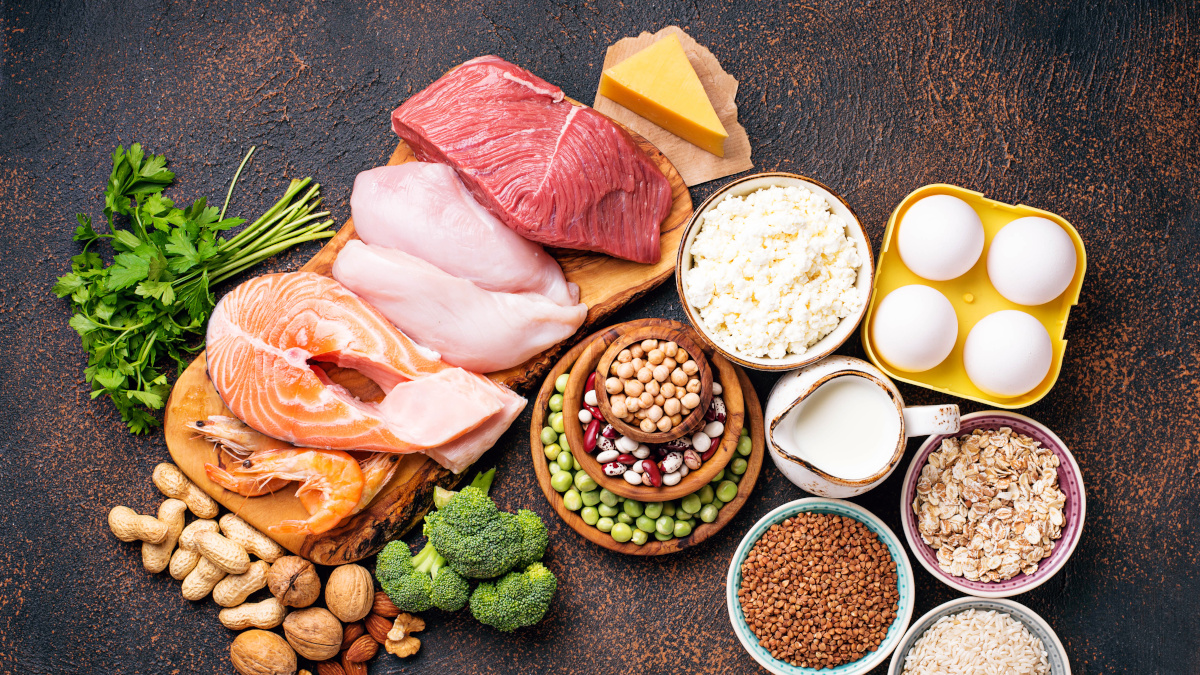
Which foods contain protein?
Proteins are the primary elements that make up meat and fish. They are also found at significant levels in seafood, eggs, dairy products, nuts and some vegetables.
To increase your protein intake, you can also incorporate whey protein into your diet (for example, with our Undenatured Whey Protein Isolate product).
What does a typical menu look like?
| Breakfast | Lunch | Dinner |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Which supplements should you take with this diet?
Note: following a high-protein diet involves reducing your intake of certain foods and may therefore lead to dietary deficiencies. In order that you don’t fall short on vitamins and minerals, it’s a good idea to take a supplement that provides certain vitamins, magnesium and calcium. We’d suggest choosing a multivitamin supplement (such as Daily 3). Make sure too that you get enough potassium and sodium.
By reducing your carbohydrate consumption, you also risk an inadequate fibre intake. So try to obtain it from other foods or from supplements (such as organic acacia gum or fructo-oligosaccharides, an excellent source of fibre).
It’s important to bear in mind that the body also needs lipids and that this diet involves a significant reduction in lipid intake. You can, however, supplement with omega-3, a fatty acid essential for good health (the best choice is Super Omega 3, the purest and most stable EPA/DHA supplement available).
References
- Moon J, Koh G. Clinical Evidence and Mechanisms of High-Protein Diet-Induced Weight Loss. J Obes Metab Syndr. 2020 Sep 30;29(3):166-173. doi: 10.7570/jomes20028. PMID: 32699189; PMCID: PMC7539343.
- Elmadfa, I.; Leitzmann, C.: « Ernährung des Menschen », Éditions Eugen Ulmer 2015, p. 142 ff.
- « Sättigung (Physiologie) », Melzer, M. (2018): « „Was Hunger auslöst, was satt macht »,
- Antonio J, Ellerbroek A, Silver T, et al. A High Protein Diet Has No Harmful Effects: A One-Year Crossover Study in Resistance-Trained Males. J Nutr Metab. 2016;2016:9104792. doi:10.1155/2016/9104792
- Bilsborough S, Mann N. A review of issues of dietary protein intake in humans. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2006 Apr;16(2):129-52. doi: 10.1123/ijsnem.16.2.129. PMID: 16779921.
Keywords
5 Hours
First bottle has been finished
First bottle has been finished. 2 bottles remaining for 3 month time frame trial as recommended
CORCORAN Pamela
5 Days
repeat customer
recommended by my doctor. easy to create an account. Discounts and specials are appreciated. packaging and delivery is dependable. Capsules easy to digest. I've had some some capsules and tablets that are broken inside their bottles.
Kokee
9 Days
Order was shipped on time and packaged…Wonderful Jobs!
Order was shipped on time and packaged excellently.
DMHoge
15 Days
great products and prices
great products and prices
Marie
21 Days
Easy to navigate site
Easy to navigate site, had what I was searching for, good price. easy order-check out
James Tucker
27 Days
My skin is clearing up nicely!
Pretty good for my skin so far.
Christian
30 Days
The new packaging is excellent
The new packaging is excellent - finally! No more squashed boxes and torn envelopes.
GORAN
30 Days
Great Product
Great Product
Larry Garrett
35 Days
Quick shipping
Quick shipping; good price. No issues!
Mary McCarty
36 Days
Thr product is very good and is helping…
Thr product is very good and is helping me on my health. Then is always on time
LUGO Luz
39 Days
Buying was fine
Buying was fine. I had problems with the website not recognizing my login info, and had to call to get it fixed. Other than that, everything was good.
David S. Clark
39 Days
Your super maca and super ginseng are…phenomenal
Your super maca and super ginseng are phenomenal supplements that compliment each other when taking them together. Fantastic feeling of well-being and lots of mid day energy without the crash.
Keith Mason
42 Days
I have had amazing results with every…
I have had amazing results with every supplement I've purchased. I am extremely satisfied with this company
kirstin Torres
42 Days
Fine products
Fine products . They are on the leading edge of online supplements. The only issue -so far-is they sometime run out of subscription items.
Jason Argos
45 Days
The ordering process is very user…
The ordering process is very user friendly and the products always come in a timely manner.
CARTER Rhonda