Everything You Need to Know About Spirulina!
One of the latest food trend among top chefs, a potential meat substitute for vegetarians, a superfood with supposedly exceptional benefits - spirulina is grabbing more and more headlines across the globe.
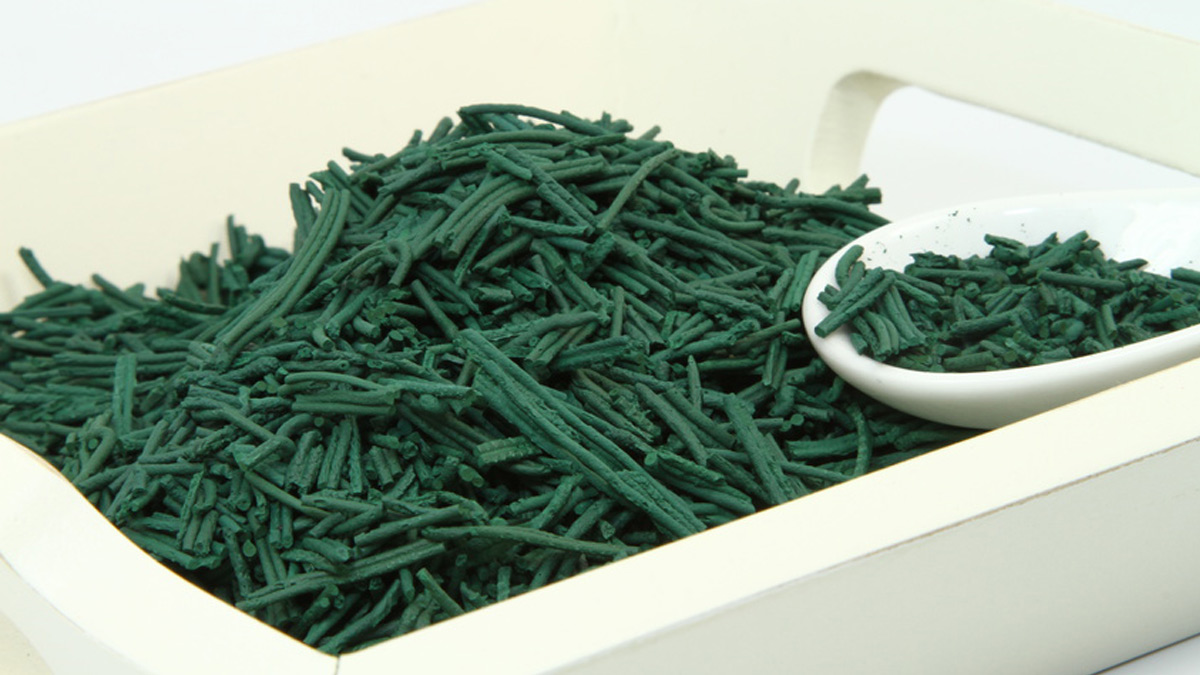

What Is Spirulina?
Spirulina is a blue-green algae, or more specifically a filamentous cyanobacteria. Thousands of species of cyanobacteria exist but only a few are edible. They include Arthrospira platensis, the main species used and sold as 'spirulina'. The name comes from the spiral shape of the Arthrospira cyanobacteria.
Where Does This Blue Algae Come From?
The blue algae Arthrospira platensis, known as spirulina, naturally grows in warm water lakes. First discovered in the lakes of Mexico and Chad, it now seems to be cultivated in many countries across the world.
What Is Spirulina Made Of?
Seemingly traditionally used for many years in Mexico and Chad for its potential high nutrient content, spirulina appears to have an interesting nutritional composition: protein (from 50 to 70%), carbohydrates (from 15 to 25%), minerals (from 7 to 13%), lipids (from 4 to 7%), as well as fiber (from 2 to 8%).
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), this micro algae could be one of the most complete foods in the world, in addition to possibly one of the main nourishment sources for the future.
What are Potential Spirulina Benefits?
Like other algae such as Chlorella and Ecklonia Cava, spirulina is considered as a superfood.
It it distinctive for its potentially high vegetable protein content with apparently strong bioavailability in the body. It also appears to help provide 8 essential amino acids: methionine, tryptophan, threonine, lysine, phenylalanine, valine, leucine, and isoleucine.
Spirulina may also be a source of other molecules needed by the body to function normally, including certain minerals and vitamins. For instance, it could be known for its possibly high content in iron and beta-carotene, a vitamin A precursor.
Omega-6 fatty acids may also have been identified in spirulina's composition, as well as the two natural pigments responsible for spirulina's blue-green color: chlorophyll and phycocyanin.
Why Take Spirulina?
With its interesting nutritional composition, this micro-algae seems to offer multiple benefits. In providing proteins, amino acids, and essential minerals, it could help support already healthy function of the body as a whole.
Its beta-carotene content may also give it a potential antioxidant effect. Certain studies appear to suggest that spirulina could help support immune system function and maintain normal cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
How Should You Take Spirulina?
Once harvested, spirulina should be dried before being used. It is today marketed in several forms, including flakes, powder, or dietary supplements.
Keywords
173 Days
EXCELENTE TODO
EXCELENTE EN SERVICIO Y PRODUCTOS LOS RECOMIENDO¡¡ GRACIAS¡¡
ANTONIO ARRIAGA
173 Days
EXCELENTE TODO
EXCELENTE EN SERVICIO Y PRODUCTOS LOS RECOMIENDO¡¡ GRACIAS¡¡
ANTONIO ARRIAGA
173 Days
EXCELENTE TODO
EXCELENTE EN SERVICIO Y PRODUCTOS LOS RECOMIENDO¡¡ GRACIAS¡¡
ANTONIO ARRIAGA
368 Days
Productos de excelente calidad!
Productos de excelente calidad!
CRUZ Francisco
368 Days
Productos de excelente calidad!
Productos de excelente calidad!
CRUZ Francisco
368 Days
Productos de excelente calidad!
Productos de excelente calidad!
CRUZ Francisco
457 Days
Suplementos de calidad
Me encantan los probioticos de esta empresa empeze a leer el libro "el revolucionario mundo de los probioticos" Esta empresa tiene todos los probioticos que este libro menciona en ningun lugar los eh podido encontrar solo en Super Smart Los resultados que hemos obtenido en nuestra salud con los probioticos que solo se encuentran en esta empresa an sido sorprendentes. Muy muy agradecida con Super Smart . Si tuvira mil estrellas se las daría.
Cliente
457 Days
Suplementos de calidad
Me encantan los probioticos de esta empresa empeze a leer el libro "el revolucionario mundo de los probioticos" Esta empresa tiene todos los probioticos que este libro menciona en ningun lugar los eh podido encontrar solo en Super Smart Los resultados que hemos obtenido en nuestra salud con los probioticos que solo se encuentran en esta empresa an sido sorprendentes. Muy muy agradecida con Super Smart . Si tuvira mil estrellas se las daría.
Cliente
457 Days
Suplementos de calidad
Me encantan los probioticos de esta empresa empeze a leer el libro "el revolucionario mundo de los probioticos" Esta empresa tiene todos los probioticos que este libro menciona en ningun lugar los eh podido encontrar solo en Super Smart Los resultados que hemos obtenido en nuestra salud con los probioticos que solo se encuentran en esta empresa an sido sorprendentes. Muy muy agradecida con Super Smart . Si tuvira mil estrellas se las daría.
Cliente
483 Days
High quality vitamins!
High quality vitamins!
François-Xavier Yang-Ting
577 Days
Siempre muy conforme
Siempre muy conforme
VINAS Marta Noemi
577 Days
Siempre muy conforme
Siempre muy conforme
VINAS Marta Noemi
577 Days
Siempre muy conforme
Siempre muy conforme
VINAS Marta Noemi
909 Days
Productos excelentes
Productos excelentes Entrega a tiempo
VINAS Marta Noemi
909 Days
Productos excelentes
Productos excelentes Entrega a tiempo
VINAS Marta Noemi